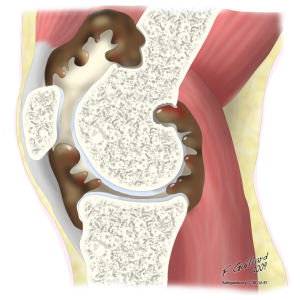
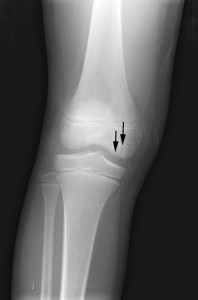
Those in the world of sports physiotherapy would be aware of the frequency with which we encounter episodes of patellar instability. Whilst much research is performed in the adult population, it is important to recognise patellar dislocation as one of the most common acute knee injuries in children. Accordingly, this article will discuss new research into the predictors of patellofemoral joint instability in the adolescent and paediatric populations.
It is no secret that sports physiotherapists and physical therapists across the world commonly assess and treat knee injuries. Of these injuries, patellofemoral pain is exceptionally common, accounting for 25% of all sports related knee injuries (Fredericson & Yoon, 2006). In fact, patellofemoral pain syndrome is the most commonly reported injury sustained by runners (Taunton et al., 2002). As many of the aetiological factors that contribute to patellofemoral pain syndrome have not been clearly identified, decision making regarding appropriate rehabilitation and treatment can often be challenging. This article will discuss the use of isometric adduction during closed kinetic chain lower limb exercises to facilitate vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) activation.
The post-operative rehabilitation of an ACL reconstruction is something that many sports physiotherapists perform on a daily basis. Many will know that muscular atrophy is quite common; particularly affecting the quadriceps, hamstrings and triceps surae. In fact, quadriceps atrophy and strength will often exceed 20% during the first three months (Nicholas et al., 2001). Therefore, we see post-operative rehabilitation protocols focusing on quick restoration of the patients muscle function and strength. Thus, we are often quick to, and appropriately so, prescribe exercises. However, this article will discuss the potential for the additional clinical benefits of electrical muscle stimulation (electro-stimulation)
Any physiotherapist working with academy footballers will know that these players are at risk of overuse injuries due to their immature musculoskeletal systems (1). However, it is imperative that therapists can confidently identify when the players require a therapeutic intervention rather than dismissing their symptoms as ‘growing pains’. It has been found that 5% of all injuries in football academies are due to overuse (1), as some young footballers will partake in high volumes of physical activity. This article will discuss the evidence based management of Osgood-Schlatters condition.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome is a condition that is commonly encountered by the sports physiotherapist. There is a clear reason for this, it has been reported to affect approximately 25% of athletes (DeHaven & Lintner, 1986). Furthermore, it is the most commonly reported injury sustained by runners (Taunton et al., 2002). Thus, it is the subject of much discussion on this site, and we have provided articles on a number of management options for patellofemoral pain syndrome. However, this article will discuss new research on potential prospective indicators for the development of patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Now, I’m not hear to scare you. But there are many conditions out there that are so uncommon that we often don’t even know that they exist. Unfortunately, sometimes these conditions may walk into our clinics and have us shaking our heads in disbelief and asking ourselves… ‘why don’t you fit into that diagnosis!’. I think for many pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS) of the knee is one of these diagnoses. It is quite rare, however, it presents similarly to many of the conditions that we as sports physiotherapists treat on a daily basis. This article discusses PVNS including assessment, diagnosis, and the treatment options.
In the world of sports physiotherapy the assessment and diagnosis of knee pathology is a daily event. As we are all well aware, an accurate diagnosis is achieved only via a skilled subjective and objective examination. Thus, sports physiotherapists will regularly rely on the results of special orthopaedic or clinical tests to make a diagnosis. This is well covered ground on this site, as we regularly the discuss the diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for common conditions. However, there is always new research regarding the accuracy of existing techniques and the development of new ones. This leads to new research on the use of joint line fullness to assist in the diagnosis of meniscal tears. This article will discuss the technique and its potential clinical utility.
In the sports physiotherapy world we are frequently called upon to assess and treat athletes of all ages. As you might expect, this may range from young children through to nonagenarian Master’s athletes. Sports physiotherapists would know when dealing with young athletes missing a career-ending (yes, career) diagnosis can be unforgivable. One such diagnosis is juvenile osteochondritis dissecans of the knee, a condition that commonly affects athletic children, and one that if left unchecked could jeopardise the integrity of their knee. Thus, accurate and timely diagnosis followed by appropriate management is essential when dealing with juvenile osteochondritis dissecans…..
In this episode of the podcast I interview Jonathan Mulford. Dr Mulford is an Orthopaedic Surgeon who specialises in all aspects of knee surgery. He graduated from the University of Tasmania with Honours in 1995, and completed his orthopaedic training in Sydney in 2005. In addition to his clinical work he has a strong interest in clinical research, and has just authored a systematic review on the use of the LARS ligament.
 TSP 008: LARS/ACL Reconstruction with Jonathan Mulford [ 29:43 ] Play Now | Play in Popup | Download
TSP 008: LARS/ACL Reconstruction with Jonathan Mulford [ 29:43 ] Play Now | Play in Popup | Download
Patellar tendinopathy is a common overuse injury of the patella tendon frequently seen in running and jumping sports. As many as 53% of athletes retire from their sports due to this injury, highlighting the importance of knowledge and up to date research in such an area to provide optimal treatment (van Ark et al, 2011). The utilisation of injection therapy has recently gained popularity and a number of studies have investigated the clinical benefits and pathological results of the various injection options. This article will discuss new research on the efficacy of injection treatments for patellar tendinopathy.
In the past this site has featured some lighter, colloquial blog posts. These articles discuss issues related to the greater physiotherapy community. Thus, I present a few mantras I have heard, adapted or made up for the physios to live by in the coming year.
Radial tunnel syndrome is rare, it is challenging to differentially diagnose and can be a monster to manage. If you have a recalcitrant case of tennis elbow then this post will interest you! This article discusses the best available evidence for assessment and management of radial tunnel syndrome.