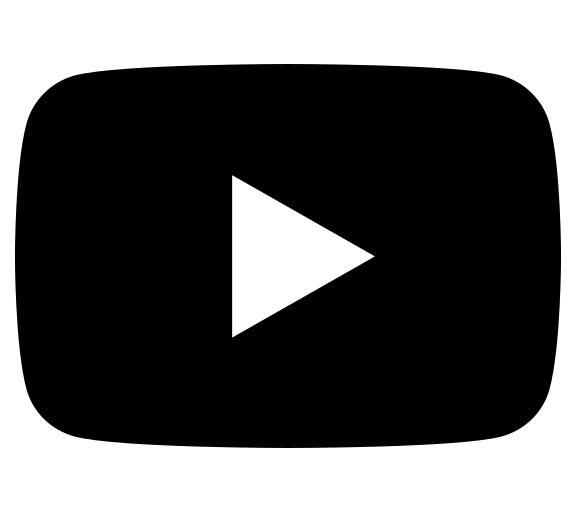
Groin pain is a common complaint in sports involving running, kicking and explosive changes of direction, and as such is frequently encountered by the sports physiotherapist. In soccer, groin and lower abdominal pain accounts for 10-13% of injuries per year. However, due to the number of potential differential diagnoses for athletes with chronic pain in the groin and lower abdominal region only a small proportion of athletes are eventually diagnosed with athletic pubalgia (sports hernias). Athletic pubalgia is a poorly understood disease process and it is imperative that athletes with the condition are managed appropriately as the symptoms can eventually limit the athlete’s participation in training and playing.
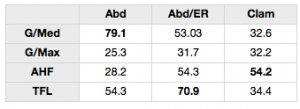
It has been suggested that up to 79% of runners will sustain lower limb injuries. The patients with these pathologies frequently present with identifiable biomechanical faults associated with either deficits in pelvic strength or neuromuscular function. Thus, physiotherapists and physical therapists the world over implement rehabilitation programs aimed at strengthening the lateral hip abductors and external rotators. However, when it comes to exercise prescription for this musculature we require EMG studies to ensure that we are operating from a strong evidence basis. This article discusses such research.
In this episode of the podcast I interview Trent Salkavich. Trent is a Sports Podiatrist and Director of SportsPodiatrists.com.au. He consults from Sydney Sports Medicine Centre, Balmain Sports Medicine and Sydney Sports Med Specialists. He is currently the consulting podiatrist for the Australian Defence Force Academy Barracks, Sydney Apia (formally known as the Medibank) International Tennis Tournament, NSWIS/AIS Tennis players, various AUS/NSW Institute of Sport athletes, and the Australian Wallabies 2011 World cup team.
 TSP009: Footwear Prescription for Running with Trent Salkavich [ 33:18 ] Play Now | Play in Popup | Download
TSP009: Footwear Prescription for Running with Trent Salkavich [ 33:18 ] Play Now | Play in Popup | Download


